Web templates allow MyST to render documents as HTML-based sites.
These provide different reading experiences that are designed for different types of MyST documents.
They are defined via the same templating system used for static document exporting, and a base set of web themes can be found in the jupyter-book/myst-theme repository.
If you want to build or ship your own theme, see the developer guide in Develop a MyST Web Theme.
Themes bundled with MyST¶
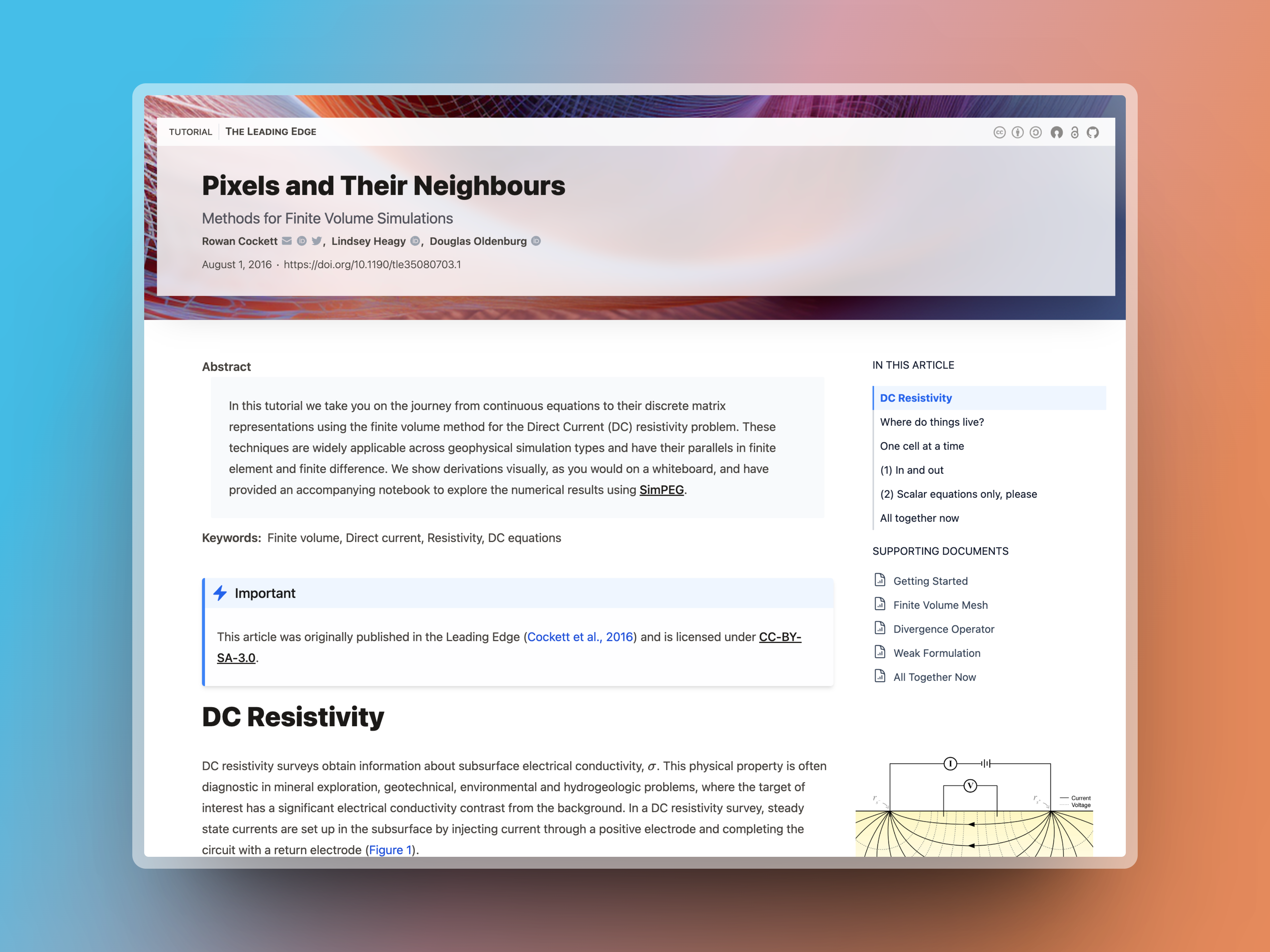
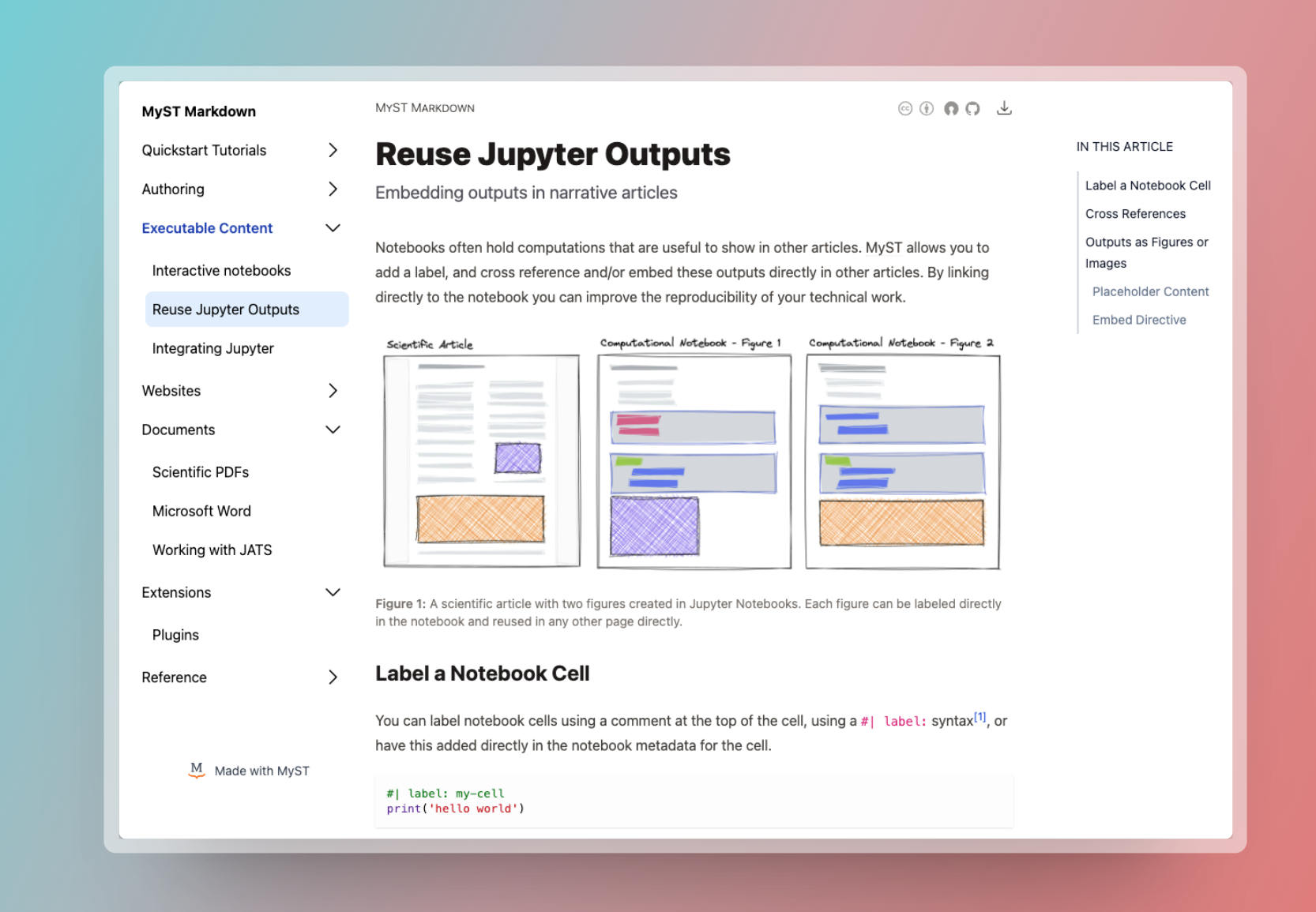
There are two templates for MyST websites, a book-theme, which is the default and is based loosely on Jupyter Book and an article-theme that is designed for scientific documents with supporting notebooks. The documentation for this site uses the book-theme. For a demonstration of the article-theme, you can see an article on finite volume.
Article Theme¶
The article theme is centered around a single document with supporting content, which is how many scientific articles are structured today: a narrative article with associated computational notebooks to reproduce a figure, document data-cleaning steps, or provide interactive visualization. These are listed as “supporting documents” in this theme and can be pulled in as normal with your Table of Contents. For information on how to import your figures into your article, see Embed and Reuse Jupyter Outputs.
The frontmatter that is displayed at the top of the article is the contents of your project, including a project thumbnail and banner. The affiliations for your authors, their ORCID, email, etc. are available by clicking directly on the author name.
Change Site Templates¶
To manually specify your website template, use the site.template property:
1 2 3 4project: ... site: template: article-theme
Change the template property to article-theme.
Site Options¶
Site options allow you to configure a theme’s behavior.[1]
These should be placed in the site.options in your myst.yml.
For example:
site:
options:
favicon: my-favicon.ico
logo: my-site-logo.svgBelow is a table of options for each theme bundled with MyST.
book-theme template¶
Simple site for displaying multiple articles and notebooks with a table of contents.
- Options
- hide_toc (boolean)
Hide the table of contents
Hide the previous/next links in the footer
- hide_outline (boolean)
Hide the document outline on all pages
- hide_title_block (boolean)
Hide the document title on all pages
- hide_search (boolean)
Disable the search
- outline_maxdepth (number)
The maximum depth to show on the document outline, for example,
2would show only two depths of headings (e.g.<H1>and<H2>)- twitter (string)
Twitter handle related to the site
- favicon (file)
Local path to favicon image
- logo (file)
Local path to logo image
- logo_dark (file)
Local path to logo image for dark mode
- logo_text (string)
Short text to display next to logo at the top of all pages
- logo_url (string)
If specified, link logo to this URL. Otherwise, point to root page.
- analytics_google (string)
Google analytics key
- analytics_plausible (string)
Plausible analytics key
- numbered_references (boolean)
Show references as numbered, rather than in APA-style. Only applies to parenthetical citations
- folders (boolean)
Respect nested folder structure in URL paths
- style (file)
Local path to a CSS file
article-theme template¶
Simple site for displaying an article with associated notebooks.
- Options
- hide_toc (boolean)
Hide the table of contents
Hide the previous/next links in the footer
- hide_outline (boolean)
Hide the document outline on all pages
- outline_maxdepth (number)
The maximum depth to show on the document outline, for example,
2would show only two depths of headings (e.g.<H1>and<H2>)- twitter (string)
Twitter handle related to the site
- favicon (file)
Local path to favicon image
- logo (file)
Local path to logo image
- logo_dark (file)
Local path to logo image for dark mode
- logo_text (string)
Short text to display next to logo at the top of all pages
- logo_url (string)
If specified, link logo to this URL. Otherwise, point to root page.
- analytics_google (string)
Google analytics key
- analytics_plausible (string)
Plausible analytics key
- numbered_references (boolean)
Show references as numbered, rather than in APA-style. Only applies to parenthetical citations
- folders (boolean)
Respect nested folder structure in URL paths
- style (file)
Local path to a CSS file
Folder-based URL structures¶
By default, MyST URLs only contain the file name for each page, not folder names. To maintain nested folder structure in the URLs (e.g., folder/page.md -> /folder/page/), use site.options.folders like so:
1 2 3 4 5 6... site: template: book-theme options: folders: true ...
Example of setting folders to true to show nested file structure in the URL
Use index files as folder landing pages¶
With folders: true, you can use index.md (or readme.md) inside a folder as a landing page for that folder.
This lets you organize all of a section’s content in a single folder:
getting-started/
├── index.md # Landing page at /getting-started/
├── install.md # /getting-started/install/
└── configuration.md # /getting-started/configuration/Page Options¶
Any option from site.options can be overridden per-page in the frontmatter under the site key.
Note that the nesting is different: options are placed directly under site: in page frontmatter, not under site.options:.
---
...
site:
hide_toc: true # This is site.options.hide_toc in myst.yml
---Other top-level site configuration¶
There are some other top-level site configuration options not documented here. You can find them in the following two files.
packages
packages
They are generally unique to the theme (and thus in a dedicated
site.optionskey rather than a top-level option insite).